Get a whiter smile but make informed decisions
At-home teeth whitening kits promise convenience and fast results from home. Although they can lighten surface stains, their efficacy and safety depend on the product’s composition, gel concentration, and correct use. It is key to know the risks, professional alternatives, and when to see a dentist.
How do at-home teeth whitening kits work?
The kits usually include a splint (or trays) and a gel with hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide in low concentrations. The gel penetrates the enamel and oxidizes the molecules causing the stains, achieving gradual lightening. Commercial formulations and the duration
of applications determine the degree of lightening.
Advantages they offer (and why we should be cautious)
- Convenience: the treatment is done at home at your own pace.
- Cost: they are usually more affordable than professional treatments.
- Accessibility: they are easily purchased in pharmacies and online stores.
However, the ease of acquisition can encourage inappropriate or prolonged use that increases tooth sensitivity, enamel damage, or gingival irritation. That is why the economic and practical benefits often do not compensate for the risks if there is no professional supervision.
Safer and more effective professional alternatives
- Professional in-office whitening: performed by a dentist with medical-grade products and exposure control for fast and safe results. Consult our guide on teeth whitening in Guatemala.
- Custom trays with professional gel: manufactured by the dentist for a better fit and contact of the gel with the dental surface.
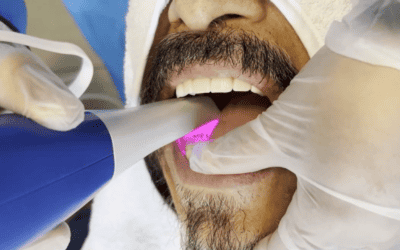
- Laser or light-assisted therapies: accelerate the action of the gel under clinical supervision.
Who should not use kits without supervision?
People with inflamed gums, active cavities, extensive restorations (crowns, veneers), or severe sensitivity should consult before using kits. Whitening does not change the color of crowns or veneers and can generate aesthetic differences.
Common ingredients and their impact
Hydrogen peroxide / carbamide peroxide: whitening agents; low concentrations are less effective but safer.
Carbopol and glycerin: improve the adhesion and texture of the gel.
Aromas and colorants: to improve the experience, without whitening effect.
Remember that home products contain a lower concentration than clinical ones; therefore, their results are more limited.
Hygiene and recommendations during any whitening treatment
- Brush and floss before each application to remove biofilm and improve gel contact with the enamel.
- Avoid staining foods and drinks (coffee, tea, red wine) during and after treatment.
- If sensitivity or irritation appears, discontinue use and consult your dentist.
Natural alternatives: caution
Remedies such as baking soda or coconut oil lack solid evidence and, used frequently, can wear down the enamel. Always consult with a professional.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are at-home teeth whitening kits safe?
They can be if used according to instructions and if there are no prior oral issues, but professional supervision always reduces risks.
When are results visible?
It depends on the product and the stain; in general, weeks of intermittent use for visible changes.
Can they damage enamel?
Excessive use or improper concentration can increase sensitivity and, in extreme cases, affect the tooth surface.
Do they affect restorations?
They do not whiten crowns, veneers, or resins: different shades could remain.
What do I do if I have sensitivity?
Suspend treatment and consult your dentist; desensitizing gels and protocols exist.
Conclusion and call to action
At-home teeth whitening kits offer convenience and can improve tooth tone in surface stains, but their use without professional evaluation involves risks. If you are looking for faster, longer-lasting, and safer results, consider professional in-office options or custom trays.
For an assessment and recommendations adapted to your case, schedule a consultation at Contact iSmile Guatemala or review our guide on teeth whitening.